Identifying and Addressing Potential Faults in Transformers
Identifying and Addressing Potential Faults in Transformers
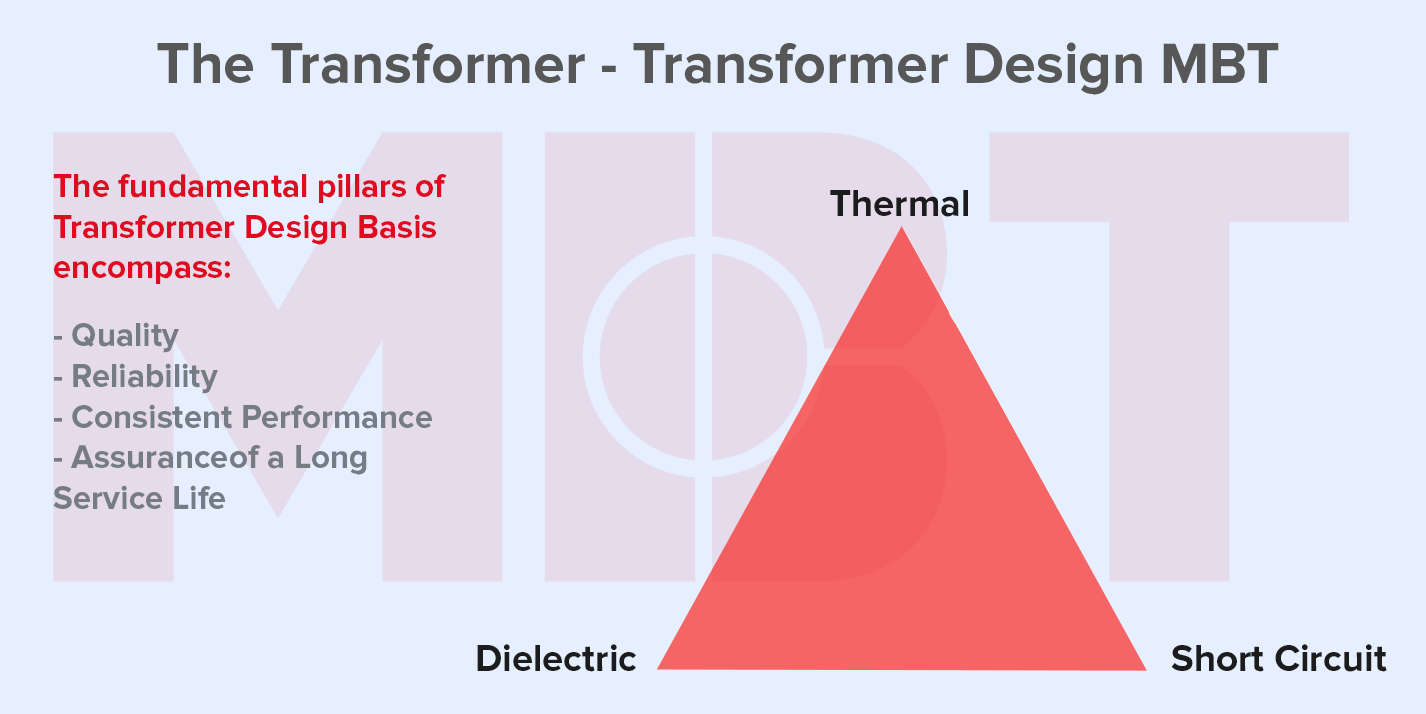
Transformers play a pivotal role in power distribution systems, serving as vital components that step up or step down voltages for efficient transmission. Despite their reliability, transformers are susceptible to various faults that can disrupt their functionality. Understanding these potential issues and promptly addressing them is crucial for ensuring the seamless operation of electrical networks.

Common Transformer Faults
1. Overheating: Excessive heat is a frequent issue in transformers, often caused by overloading, poor ventilation, or high ambient temperatures. This can lead to insulation degradation and, if left unchecked, may result in winding failure.
2. Insulation Breakdown:Insulation breakdown occurs due to voltage surges, moisture ingress, or aging. This can cause short circuits between windings and compromise the transformer's efficiency.
3. Winding Failures: Winding faults, including open circuits or short circuits in the coil windings, are common. These faults may result from mechanical stresses, manufacturing defects, or insulation degradation.
4. Oil Contamination: Transformers using oil for insulation and cooling are prone to oil contamination, which can lead to decreased dielectric strength and insulation failure.
5. Corrosion and Rust: External factors like environmental conditions can cause corrosion or rust on the transformer's surface, potentially leading to structural weaknesses and reduced lifespan.
Detecting Transformer Faults
Early detection of transformer faults is critical to prevent extensive damage. Routine inspections, thermal imaging, dissolved gas analysis (DGA), and insulation resistance tests are effective diagnostic tools.
Addressing Faults
Upon identifying a fault, immediate action is necessary to avoid widespread system disruption:
1. Isolation: Isolate the faulty transformer from the network to prevent further damage and ensure safety.
2. Repairs or Replacement: Depending on the fault's severity, repairs or replacement of damaged components may be necessary. This includes rewinding coils, repairing insulation, or replacing corroded parts.
3. Oil Purification: For oil-filled transformers, purifying or replacing contaminated oil is crucial to restore dielectric strength and maintain optimal performance.
4. Upgrading Protection Systems: Implement enhanced protection systems such as relays, surge arrestors, and monitoring devices to prevent future faults.
Conclusion
Transformers are indispensable in power transmission, yet they are vulnerable to various faults that can disrupt operations. Proactive maintenance, regular inspections, and prompt resolution of identified issues are essential in ensuring the reliability and longevity of transformers within electrical networks. By addressing potential faults swiftly, the efficiency and safety of the entire power system can be preserved.
*Keywords: transformer faults, transformer overheating, insulation breakdown, winding failures, oil contamination, corrosion, rust, detecting transformer faults, addressing transformer faults, transformer maintenance, power distribution systems.
Refer to:
If you are interested in exporting MBT transformers or need to learn more about our products, please contact us. We will be very happy to assist you
CONTACT INFO:
– Email : Info@mbt.vn
– Phone: +84.913.006.538
– Fax : +84.43.765.3511
– Address: Song Cung Industrial Site, Dong Thap commune, Dan Phuong district
– Website : https://www.mbt.com.vn – https://vietnamtransformer.com/
– Fanpage : https://www.facebook.com/mbt.com.vn
– Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/@mbtvietnam