What is the main source of energy in the future - MBT electrical equipment
What is the primary energy source of the world?
Maybe you are finding the main source of energy, what is the main source of energy on earth, or what is the primary source of energy today, this article can give you the latest information of what you are finding.
Table of content:
Based on the percentage of each source to global energy consumption in the past five decades and the static figure of IEA (International Energy Agency), MBT Electric give you the world's eight most-used energy sources in 2020
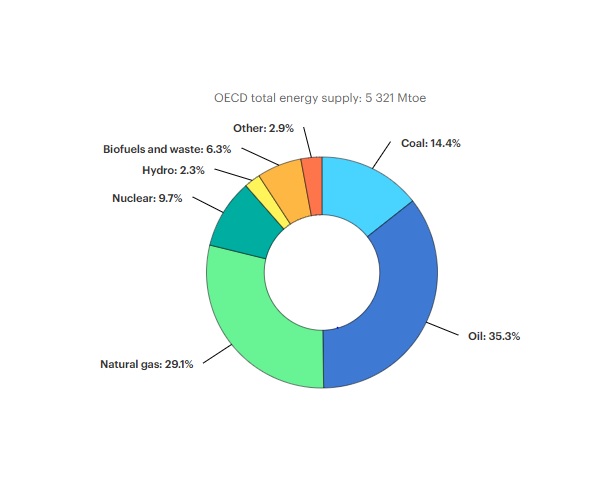
Static figure in 2019 – origin: iea.org
1. Coal: 14.4%
Coal is the "heart" of fossil fuels.
All over the world, the wind is changing. Chinese President Xi Jinping was surprised when he set a goal by 2060 to reduce China's net carbon emissions to zero.
The President-elect of the United States, Mr. Joe Biden, will bring the US back to the Paris agreement on climate change. In the financial market, clean energy companies are thriving, with the most eloquent proof that Tesla recently joined the S&P 500 and became one of the largest members of the index.
Not only words, but nations have also taken real action. In the US and Europe, coal consumption – the most significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions – has fallen by about 34% since 2009. International Energy Agency IEA said that global coal consumption would never be able to exceed the pre-Covid-19 peak.
Of course, coal still plays an important role in our lives. Coal accounts for about 27% of the raw materials used to power everything from cars to power plants. Unlike natural gas and petroleum, coal is concentrated carbon and accounts for 39% of the annual fossil fuel CO2 emissions. Now the mission is to replicate the success of Europe in Asia. It is not easy.
2. Oil: 35.3 %
On an industrial scale, in the world, oil has been exploited since the 19th century in three countries: the US, Russia, and Romania. By the early 20th century, oil was used in 20 countries but concentrated mainly in three countries: the US, Venezuela, and Russia. By 1940, oil had been extracted in more than 40 countries and focused mostly in the US, Soviet Union, Venezuela, and Iran. The number of oil-producing nations in 1970 had risen to 60, and by the end of 1990, it was 95.
During the 1960s, more than half of oil production was in the Western Hemisphere, but then the dominance gradually belonged to Eastern Hemisphere countries.
The EIA forecasts crude oil production from the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) will average 27.2 million barrels a day by 2021, up from an estimated 25.6 million barrels a day in 2020. Output growth forecasts reflect OPEC's increase in Libya's production and production targets continuing to rise. On 5 January 2021, OPEC and its partner countries (OPEC +) announced that they would maintain a previously agreed production that increases 0.5 million barrels per day. The latest OPEC + agreement also calls for Russia and Kazakhstan to increase production in February and March. However, Saudi Arabia's additional voluntary cuts in February and March resulted in lower overall OPEC + output in early 2021. The EIA forecasts OPEC crude production to increase by 1, 1 million barrels/day by 2022.
3. Natural gas: 29.1%
Natural gas is the cleanest and fastest-growing fossil fuel, contributing nearly a third of total energy demand growth in the past decade, more than any other fuel.
Today, natural gas accounts for 23% of global primary energy demand and nearly a quarter of electricity production.
As the cleanest burning fossil fuel, natural gas offers several environmental benefits over other fossil fuels, especially air quality and greenhouse gas emissions..
4. Nuclear: 9.7%
About 440 nuclear power reactors generate about 10% of the world's electricity. About 50 more reactors are under construction, equivalent to about 15% of the existing capacity.
In 2019, nuclear plants provided 2657 TWh of electricity, up from 2563 TWh in 2018. 2019 is the seventh consecutive year that global nuclear power output has increased, with the output of 311 TWh higher than 2012. .
5. Hydro: 2.3%
According to the IHA and team of researchers and analysts:
Covid-19 emphasized the hydroelectric sector's resilience and its essential role in providing clean, reliable, and affordable energy, especially in crisis times.
A bold and ambitious green recovery plan involving substantial investment in sustainable hydropower will be part of the country's policy.
Global hydroelectricity installed capacity will reach 1,308 gigawatts (GW) by 2019.
Clean electricity output from hydropower reached a record 4,306 terawatt-hours (TWh), the enormous contribution from renewable energy sources.
Wind power is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies. Usage is on the rise worldwide, in part because costs are falling.
According to the latest IRENA data, globally installed electricity generation capacity on land and offshore has increased by nearly 75 over the past two decades, up from 7.5 gigawatts (GW) in 1997 to about 564 GW. in 2018. Wind power output doubled from 2009 to 2013, and in 2016, wind power accounted for 16% of electricity generated from renewable energy. Many parts of the world have strong wind speeds, but the best places to generate wind energy are sometimes remote. Offshore wind power offers enormous potential.
6. Solar and wind energy: 2.9 %
Anyone who follows developments in the energy sector will know that solar is not just the future but the present. According to the International Energy Agency's 2020 World Energy Outlook, photovoltaic solar power has been the cheapest electricity source in history. We are not talking about the future, but about the present, about the present installations.
For the first time, under these conditions, the fact that solar power will fulfill all demand in South Australia on 12 October won't surprise us. The continued increase in efficiency and the cost reduction of photovoltaic panels make solar energy a reasonable alternative to electricity generation. Furthermore, the technology continues to evolve, and there are still new capabilities, such as perovskites, that promise a significant increase in solar energy.
7. Biofuels and waste: 6.3%
It is forecasted that biofuel production will increase by 25% in the next five years. Global biofuel production increased by 10 billion liters in 2018 to hit a record 154 billion liters. Double compared to 2017, the 7% increase compared to the same period last year was the highest level in 5 years. Production is forecast to increase by 25% through 2024, an increase from 2018 due to better market prospects in Brazil, the United States, and especially China.
MBT is a manufacturer of distribution transformers in Vietnam, in 2021, we launch a new type of transformer for solar projects that is the r transformer. If you need a quotation, please contact us by email: info@mbt.vn or +84 913 006 538